It's a syndrome with no precise statistics concerning its frequency. However, it's not a rare syndrome. The heredity of Goldenhar syndrome hasn't elucidated yet. No gene has definitely been implicated for this syndrome up to now.
MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
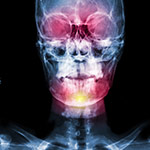
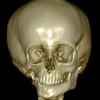
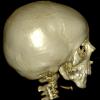
The clinical picture of Goldenhar syndrome is the same as the clinical picture of Craniofacial (Hemifacial) Microsomia, i.e. it is characterized by incomplete development of lips, ears, nose, soft palate, and mandible, usually on one side of the face. The severity of deformity varies from a barely perceptible (slight facial asymmetry, small polypoid skin morphomas in preauricular area) up to a severe degree, with severe hypoplasia of lower jaw (mandibular) and zygomatic bone as well as serious disturbance in the ear development.
ADDITIONAL ANATOMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GOLDENHAR SYNDROME
In addition to the disorders in growth that we mentioned above, The Goldenhar syndrome characterized by the presence of the following:
- Epibulbar dermoids, i.e. benign tumors (dermoid cysts) in the eye. These tumors that usually not create any problem, however, cannot be removed.
- Anatomical abnormalities in the vertebrae. They are usually detected in cervical vertebrae, but they may extend to any part of the spine.
- Abnormalities in growth of the cardiovascular, urogenital and gastrointestinal system (at lower rates).
FUNCTIONAL PROBLEMS
The functional problems of Goldenhar syndrome are the same with craniofacial (hemifacial) microsomia ones, which may occur only in severe forms of the syndrome.
- Breathlessness (shortness of breath)
- Feeding difficulty
- Ear dysplasia, when the other ear is normal then there is not any problem regarding hearing.
The Goldenhar syndrome is not associated with mental retardation.
DIAGNOSIS - ASSESSMENT
The diagnosis for the Goldenhar syndrome is done only with physical examination. The anatomical details are evaluated by a 3D CT and MRI which should not be made in infancy, unless there is a special reason. Remember that newborns and infants are extremely sensitive to radiation.
Additionally, the other systems should be evaluated too (such as skeletal, cardiovascular, urogenital, gastrointestinal, etc.).
But, the newborn should be followed up by a specialized team for the following reasons:
- The assessment must be complete
- To prevent any problems that may arise and
- To become the best possible plan for the gradual rehabilitation that will follow.
SURGICAL REHABILITATION
The surgical rehabilitation of the Goldenhar syndrome is identical to the Craniofacial (Hemifacial) Microsomia (see relevant Section). The experience has shown that the surgeries which are performed too early, must usually be repeated at a later stage, under more difficult conditions due to the scars that have been created and because the graft donor sites have already been used.
So as the child grows, there is a greater need for a satisfactory appearance in order to be accepted by his/her peers and in school, but the final procedures are transferred for a later time when the development and dentition have been advanced.