MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
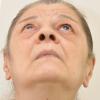
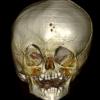
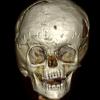
The clinical picture of Muenke syndrome is usually similar to the picture of unilateral or bilateral coronal suture craniosynostosis. The difference is that in the case of Muenke syndrome there is an obvious genetic diagnosis and inheritance (in contrast with non-syndromic types of coronal craniosynostosis).
Other morphological abnormalities that have been observed in Muenke syndrome cases are the following:
- Vaulted palate that may predispose to serous otitis
- cleft lip or/and palate (rare)
The clinical diagnosis of the syndrome requires clinical experience as well as a high index of suspicion and it is confirmed with genetic testing.
SURGICAL REHABILITATION
Unless there are specific characteristics, the surgical repair is the same as the frontal plagiocephaly repair (see relevant chapter). It is estimated that 20-25% of the cases that have been diagnosed with Muenke syndrome will need reoperation because the malformation is often profound and its full repair is very difficult to be achieved by the initial surgery.